The United States is a vast and diverse country, encompassing a wide range of climates and growing conditions. To help gardeners and horticulturists understand the suitability of plants for their specific region, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has developed a comprehensive system of hardiness zones. In this guide, we will explore the USDA Hardiness Zones of America, their significance, and how to use them for successful gardening.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is essential for gardeners and horticulturists as these zones provide valuable information about the specific climate and growing conditions in different regions of the United States. Here’s a comprehensive explanation of USDA Hardiness Zones:
1. Geographic Regions: The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) divides the country into geographic regions or zones based on their minimum average annual temperatures. Each zone represents a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference in the average minimum temperature. Zones are numbered from 1 to 13, with lower numbers indicating colder climates.
2. The USDA Hardiness Zone Map: The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is a comprehensive, color-coded map of the United States, illustrating the different hardiness zones. Gardeners and growers can use this map to identify their specific hardiness zone based on their location.
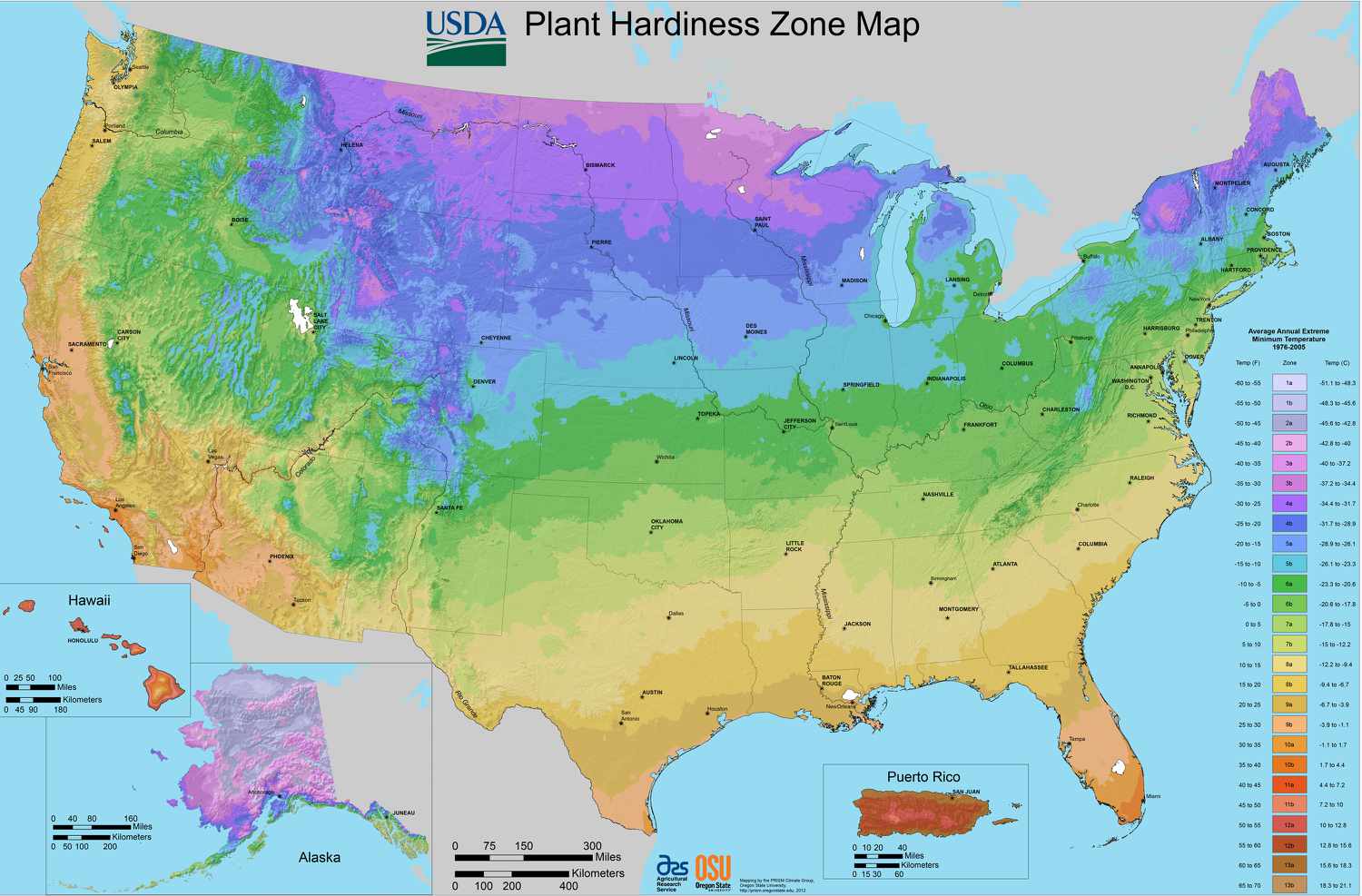
3. Zone Temperatures: Each hardiness zone has a defined temperature range, with the lowest expected winter temperature serving as the primary determinant. For example, Zone 3 has a minimum winter temperature range of -40 to -30 degrees Fahrenheit, while Zone 11 has a minimum winter temperature range of 40 to 50 degrees Fahrenheit.
4. Plant Recommendations: The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable tool for gardeners when selecting plants. Plant catalogs, nurseries, and seed packets often provide information on the recommended hardiness zones for specific plants. These recommendations help gardeners choose plants that are more likely to thrive in their local climate.
5. Frost-Free Period: USDA Hardiness Zones also play a crucial role in determining the length of the frost-free period, which is the time between the last spring frost and the first fall frost. Gardeners use this information to plan planting dates and protect their plants from frost damage.
6. Microclimates: It’s important to note that within a specific hardiness zone, there can be microclimates with slightly different growing conditions. These microclimates may be influenced by factors such as sun exposure, wind patterns, and proximity to bodies of water. Gardeners should consider these variations when selecting and caring for plants.
7. Climate Adaptation: USDA Hardiness Zones are not static and can change over time due to climate shifts. Gardeners and horticulturists should monitor any changes in their zone to adapt their gardening practices accordingly.
8. Research and Education: The USDA Hardiness Zone Map serves as a valuable resource for researchers, educators, and horticultural experts. It provides a standardized framework for understanding and communicating climate conditions and plant suitability across the country.
Significance of USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Hardiness Zones have significant importance for gardeners, horticulturists, and anyone interested in growing plants in the United States. These zones offer valuable information and serve various purposes:
- Plant Selection: The primary purpose of USDA Hardiness Zones is to assist gardeners and growers in selecting plants that are suitable for their specific region. Each plant has a recommended hardiness zone range, indicating the zones where it is likely to thrive. This information helps gardeners choose the right plants for their local climate, increasing the chances of a successful and productive garden.
- Winter Protection: Understanding your hardiness zone is essential for determining which plants may require extra protection during the winter months. Gardeners in zones with colder winters can take precautions like mulching, covering, or moving plants indoors to ensure their survival.
- Planting Dates: Hardiness zones also influence planting dates. By knowing your zone, you can determine the appropriate time to start seeds, transplant seedlings, or set out container plants to ensure they are not exposed to frost or extreme cold, thereby promoting healthy growth.
- Climate Adaptation: As climate patterns change over time, hardiness zones can shift. By tracking these shifts, gardeners can adapt their gardening practices to accommodate changing local conditions. This adaptability is essential in an era of climate change and unpredictable weather patterns.
- Local Expertise: USDA Hardiness Zones are valuable for local nurseries and gardening centers. These businesses use hardiness zones to stock plants that are suitable for their region, ensuring that customers can find plants that are more likely to thrive in the local climate.
- Efficient Gardening: Understanding your hardiness zone helps you plan your garden more efficiently. You can avoid investing in plants that are ill-suited to your climate, reducing the risk of plant stress, disease, or failure.
- Culinary Creativity: Gardeners can use their knowledge of hardiness zones to experiment with unique and seasonal ingredients, leading to culinary creativity. This experimentation results in fresh and flavorful dishes using homegrown produce.
- Community Engagement: Some gardeners open their gardens to the community, offering educational programs, workshops, and hands-on learning opportunities related to hardiness zones and gardening practices. This community engagement fosters a deeper connection to the garden and encourages others to develop their green thumbs.
- Health and Well-Being: Gardening in harmony with your hardiness zone contributes to improved health and well-being. It provides physical activity, fresh air, and the satisfaction of growing and consuming nutritious food, supporting a healthier lifestyle.
Accessing Your USDA Hardiness Zone
Accessing your USDA Hardiness Zone is a straightforward process that helps you understand the specific climate and growing conditions in your area. To determine your USDA Hardiness Zone, follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Visit the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map Website:
Go to the official USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map website. You can access it at https://planthardiness.ars.usda.gov/.
Step 2: Use the Interactive Map:
On the USDA website, you’ll find an interactive map of the United States. To access your specific hardiness zone, click on the map or enter your ZIP code in the search bar provided.
Step 3: View Your USDA Hardiness Zone:
Once you’ve entered your ZIP code or clicked on the map, the website will provide information about your specific USDA Hardiness Zone. It will also display a color-coded map that outlines the zones, helping you visually identify your region.
Step 4: Learn More:
To further explore and understand your hardiness zone, the USDA website offers additional resources, including a list of plants that are suitable for your zone and a detailed explanation of what the zone means for gardening and plant selection.
Step 5: Plan Your Garden:
Armed with knowledge about your USDA Hardiness Zone, you can now plan your garden with confidence. Select plants that are recommended for your zone, determine planting and harvesting times, and make informed decisions about winter protection for your garden.
By accessing your USDA Hardiness Zone, you’ll be better equipped to make choices that lead to a successful and thriving garden, no matter where you are in the United States. Remember that these zones are invaluable tools for both novice and experienced gardeners, helping you understand your local climate and the unique conditions that impact your plants’ growth and survival.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, understanding and using USDA Hardiness Zones is a fundamental aspect of successful gardening in the United States. By recognizing your local hardiness zone and selecting plants accordingly, you can create a garden that thrives in your climate, resulting in healthy and vibrant landscapes year after year.

